Crop protection
Technologies

Granular formulation containing Lecanicillium psallioatae is effective in controlling cardamom thrips and possess growth promoting traits also. The fungus attacks both juvenile and adults of cardamom thrips. The technology is patent filed (Patent application no. 201741044872 ). Tested and certified by a CIBRC-approved laboratory, the biopesticide has been developed in a user-friendly granular form that can be mixed with farmyard manure and applied directly to the soil.

An eco-friendly technology for managing Conogethes punctiferalis, a major pest of spice crops such as ginger, turmeric, and cardamom, has been developed using a naturally occurring entomopathogenic fungus, Metarhizium pingshaense. The technology involves spraying M. pingshaense at a concentration of 1 x 107 conidia/mL, starting from the second fortnight of July (or 45 days after planting) until the first fortnight of November, at 21-day intervals. In addition to its insecticidal action, the fungus promotes plant growth and is an effective solubilizer of zinc. It is also effective against other crambid pests affecting crops such as rice, sorghum, vegetables, and sugarcane. The technology is patent filed (Application no. 202511031583)
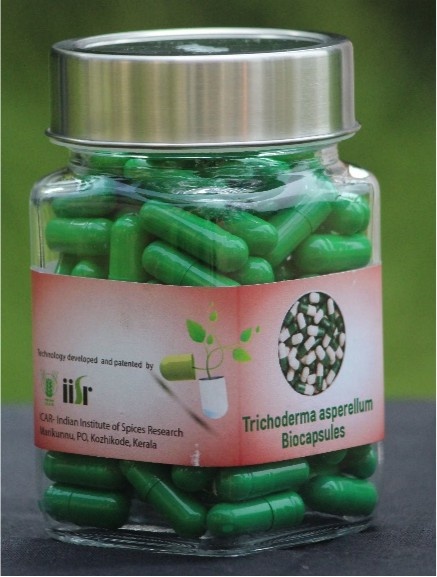

The technology (Indian Patent No: 361021 dated ;13/08/2013) involves encapsulation of the microorganisms of interest in a 1g gelatin capsule for delivery to agricultural crops. Advantages of the Technology : High microbial population (109 -1012 CFU/g.) Easy handling and storage (18-24 months).Improved shelf life (18-24 months). Low production and transportation cost. Green technology, totally ecofriendly 20-25% reduction in usage of chemical pesticides/fertilizers.




Granular lime-based microbial formulations mitigates the drawbacks of soil acidity and simultaneously delivers beneficial microbes for effective growth and establishment of crops ensuring optimal plant growth and nutrient uptake. This innovative single product can save labour cost and time involved in applying lime and beneficial organisms individually. This formulation also benefits the crop by improving the physical condition of the soil, enhancing secondary nutrient availability and by boosting soil microbial activity. The technology is patent filed (Application No: 202241010858). Available in four formulations: Tricholime & Bactolime (for acidic soils), Trichogypsum & Bactogypsum (For alkaline soils).
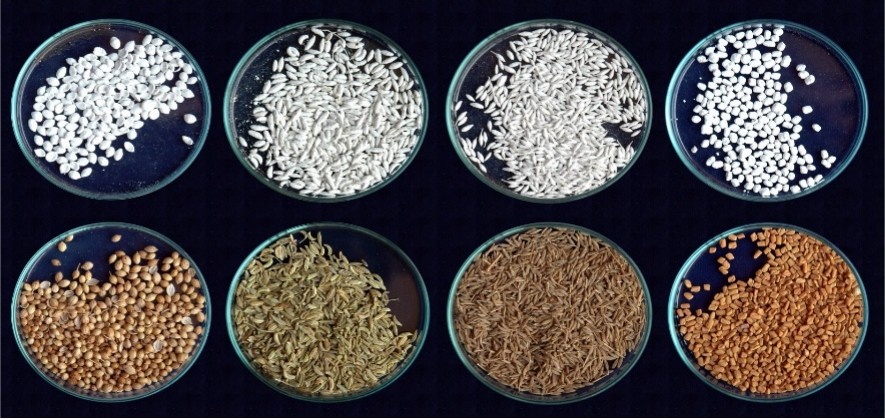

A novel process of coating beneficial microorganisms on seeds (patent no. 350698, Dated: 01.10.2013). Coated seeds exhibited longer shelf life and germination up to one year of storage in seed spices. Can be used for coating all kinds of seeds including seed spices and horticultural crops. The coated seeds can be stored at room temperature. Coated seeds are free from storage pest incidence, improve germination, enhance the yield from 15-30%.

Priming of seeds of rhizomatous and tuberous crops using Trichoderma spp, helps to shorten the germination time of rhizomes, improve the vigour of rhizome buds and also ensures uniform tiller emergence. The process also helps to prevent the growth of dry rot pathogens during storage by preventing infection and entry into the rhizome and protects the emerging crop from plant pathogens. This technology was granted patent (Patent No. 567347).

The talc formulation based on Trichoderma asperellum can be used successfully to manage soil borne fungal pathogens. It can be used in integrated disease management as well as under organic farming system in crops like black pepper, ginger, cardamom and turmeric.

Technology based on bacterial strain Bacillus licheniformis for ecofriendly management of bacterial wilt in ginger caused by Ralstonia pseudosolanacearum. The bacteria possess plant growth promoting potential besides disease control. The technology can be adopted in the integrated management of bacterial wilt in ginger. This bioagent can be applied by both seed priming and soil drenching and the strain is now available in the encapsulated form.


Plant parasitic nematodes, especially root knot nematodes (Meloidogyne spp.) cause significant damage to the plants. Currently they are managed through application of chemical nematicides like phorate and carbofuran. Biological control of root knot nematodes, therefore, is highly relevant in this context. Pochonia chlamydosporia, a known nematode biocontrol agent, is a facultative nematode parasite. It proliferates in the rhizosphere, colonizes the egg masses of root knot nematodes, and parasitizes their eggs and sedentary females.
Pochonin- Liquid formulation of Pochonia chlamydosporia contains chlamydospores which can be drenched to soil to manage nematodes. Liquid formulation has added advantage of increased shelf life too. The technology is patented (Patent No: 567444).
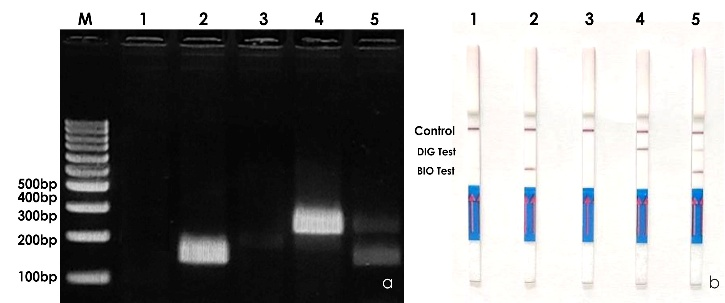
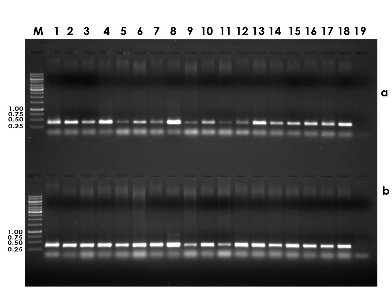
Sensitive molecular diagnostics based on polymerase chain reaction (PCR), loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP), recombinase polymerase amplification (RPA) and rapid onsite detection based on RPA-lateral flow assay (RPA-LFA) have been developed for viruses (cucumber mosaic virus, black pepper virus F and piper yellow mottle virus infecting black pepper; cardamom mosaic virus and banana bract mosaic virus infecting cardamom; ginger chlorotic fleck-associated virus 1 and 2 infecting ginger), bacteria (Ralstonia pseudosolanacearum casuing bacterial wilt in ginger), nematodes (Pratylenchus spp., Meloidogyne spp., and Radopholus similis) and oomycetes (Pythium spp., and Phytophthora spp. infecting black pepper, cardamom, ginger and turmeric). The technology can be used for the detection and certification of planting materials for freedom from pathogens.
